Organic Beet Root Powder – 6,000 mg
Beetroot, in all of its forms (powdered, blended, eaten whole – whatever!), can help athletes get a greater pump in the gym by boosting nitric oxide (NO) production via the nitrate-nitrite pathway.[1,2]
Why We Want More Nitrates (Boosting Nitric Oxide)
Whenever we consume a food high in nitrates, like beets, those nitrates are converted into NO by our salivary glands.[3-5]
The reason we want NO, and the reason it gives us a great pump, is that more nitric oxide production means more vasodilation[6] – the process by which blood vessels expand and allows more blood to flow through them.
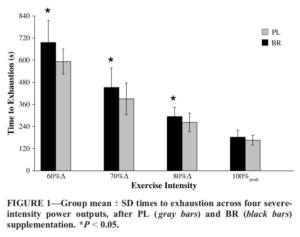
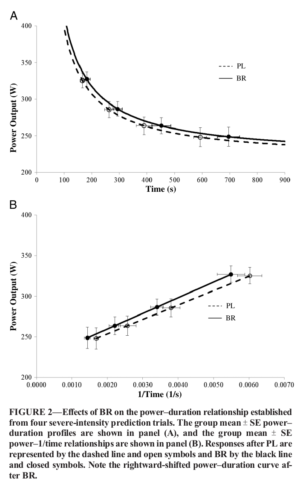
Increased blood flow means increased efficiency of oxygen and nutrient delivery, which means better performance[7,8] and faster recovery.[8,9]
In 2013, the International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism published a big meta-analysis[10] that found supplementing with nitrates can consistently increase:
- Circulation[11]
- Aerobic efficiency[11-14]
- Strength[15,16]
- Recovery speed
- Cellular energy[16-18]
- Endurance / time to fatigue[19]
Beetroot also has Betaine
Another key component of beetroot is betaine, sometimes referred to as trimethylglycine or TMG, whose ergogenic properties are well attested to in the research literature.
Similarly to creatine, betaine increases the body’s capacity to work (the definition of an ergogenic aid). But whereas creatine increases energy via phosphate donation, betaine is a methyl donor.[20] As such, it can lower blood homocysteine levels,[20] an important factor in cardiovascular health.
Betaine is also an osmolyte, a compound that positively affects the water balance in cells. Betaine supplementation can keep cells optimally hydrated[21,22] and thereby protect them against the heat shock[23] that you might experience during a long or intense athletic effort.
Although a great deal of research has corroborated the theory that betaine can increase athletic performance,[24-29] the dose used in these studies were pretty large – for example, the revolutionary studies from 2013 and 2014 that showed significant benefits in body composition from betaine supplementation? Both used a whopping 2500 milligram daily dose of pure betaine.[30,31]
Unfortunately, we probably don’t have such high amounts here – the betaine content of whole beets is only between 3 and 5 milligrams per gram.[32] So from 6 grams of beetroot powder, we could expect maybe 30 milligrams of betaine.
Nonetheless, the betaine inside could still give you some benefit, even in low concentrations – it’s just going to be more subtle than the 5 pounds of fat loss observed in the two studies we mentioned above.
Betalains: Anti-Inflammatory Pigments
As anyone who’s ever eaten beets can attest, the pigments in the bright purple vegetable are strong and intense. And although the tendency of beets to stain nearly everything they touch isn’t great, don’t let that dissuade you from trying the supplement or eating the vegetable. It turns out these pigments, called betalains, have pretty phenomenal health benefits.
Pigments like betalains are commonly used incosmetics, but it has numerous additional purposes: plants evolve these compounds because they’re potent chemical defenses, helping to protect the plant against microorganisms, fungi, and even insects.[33] Betalains can actually destroy microbes by attacking their cellular membranes![34]
Betalain-containing betanin, a natural food coloring derived from beets, has long been known to have potent anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.[33]
Given the close connection between chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and diabetes, it isn’t totally surprising that when researchers administered a betalain-rich extract sourced from chard (a cultivar of the beet leaf) to diabetic mice, they actually showed a significant decrease in their excessively high blood sugar levels[35] – a pretty impressive 40% reduction.
That’s potentially due, at least in part, to the high quercetin concentrations found in beets.[36] Quercetin is an awesome antioxidant that we’ve written about many times before. Among other properties, it has the ability to block the action of an intestinal transporter called glucose transporter 2.[36] By inhibiting GLUT-2, quercetin helps partially prevent the absorption of whatever carbohydrates you’ve ingested, thus keeping your blood sugar levels within acceptable bounds.[36]
Betalains have also been shown to inhibit plaque formation in Alzheimer’s[37] through its anti-oxidant effects, and may even inhibit the growth of cancer cells.[38]
Source link